Page 144 - Science Class 07
P. 144
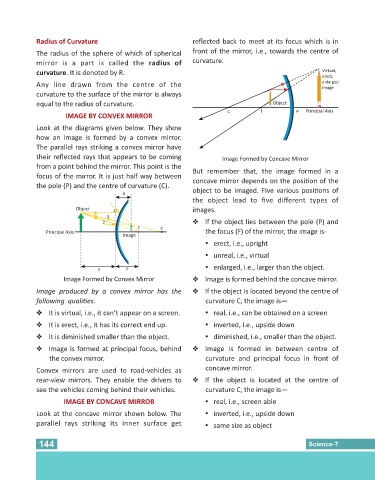
Radius of Curvature reflected back to meet at its focus which is in
The radius of the sphere of which of spherical front of the mirror, i.e., towards the centre of
mirror is a part is called the radius of curvature.
curvature. It is denoted by R. Virtual,
erect,
Any line drawn from the centre of the enlarged
image
curvature to the surface of the mirror is always
equal to the radius of curvature. Object
C f P Principal Axis
IMAGE BY CONVEX MIRROR
Look at the diagrams given below. They show
how an image is formed by a convex mirror.
The parallel rays striking a convex mirror have
their reflected rays that appears to be coming Image Formed by Concave Mirror
from a point behind the mirror. This point is the
But remember that, the image formed in a
focus of the mirror. It is just half way between
concave mirror depends on the posi on of the
the pole (P) and the centre of curvature (C).
q object to be imaged. Five various posi ons of
the object lead to five different types of
Object 1 images.
3
2 v If the object lies between the pole (P) and
F C
Principal Axis the focus (F) of the mirror, the image is-
Image
Ÿ erect, i.e., upright
Ÿ unreal, i.e., virtual
P f Ÿ enlarged, i.e., larger than the object.
Image Formed by Convex Mirror v Image is formed behind the concave mirror.
Image produced by a convex mirror has the v If the object is located beyond the centre of
following quali es. curvature C, the image is—
v It is virtual, i.e., it can’t appear on a screen. Ÿ real, i.e., can be obtained on a screen
v It is erect, i.e., it has its correct end up. Ÿ inverted, i.e., upside down
v It is diminished smaller than the object. Ÿ diminished, i.e., smaller than the object.
v Image is formed at principal focus, behind v Image is formed in between centre of
the convex mirror. curvature and principal focus in front of
Convex mirrors are used to road-vehicles as concave mirror.
rear-view mirrors. They enable the drivers to v If the object is located at the centre of
see the vehicles coming behind their vehicles. curvature C, the image is—
IMAGE BY CONCAVE MIRROR Ÿ real, i.e., screen able
Look at the concave mirror shown below. The Ÿ inverted, i.e., upside down
parallel rays striking its inner surface get Ÿ same size as object
144 Science-7