Page 33 - Science Class 08
P. 33
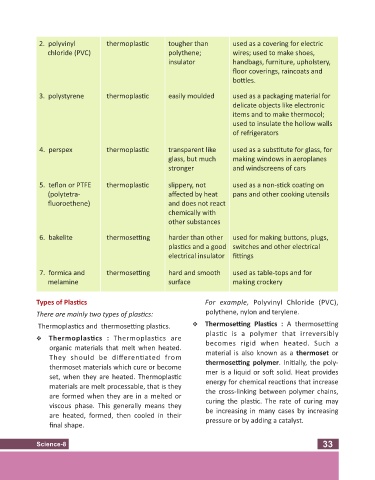
2. polyvinyl thermoplas c tougher than used as a covering for electric
chloride (PVC) polythene; wires; used to make shoes,
insulator handbags, furniture, upholstery,
floor coverings, raincoats and
bo les.
3. polystyrene thermoplas c easily moulded used as a packaging material for
delicate objects like electronic
items and to make thermocol;
used to insulate the hollow walls
of refrigerators
4. perspex thermoplas c transparent like used as a subs tute for glass, for
glass, but much making windows in aeroplanes
stronger and windscreens of cars
5. teflon or PTFE thermoplas c slippery, not used as a non-s ck coa ng on
(polytetra- affected by heat pans and other cooking utensils
fluoroethene) and does not react
chemically with
other substances
6. bakelite thermose ng harder than other used for making bu ons, plugs,
plas cs and a good switches and other electrical
electrical insulator fi ngs
7. formica and thermose ng hard and smooth used as table-tops and for
melamine surface making crockery
Types of Plas cs For example, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC),
There are mainly two types of plas cs: polythene, nylon and terylene.
Thermoplas cs and thermose ng plas cs. v Thermose ng Plas cs : A thermose ng
plas c is a polymer that irreversibly
v Thermoplas cs : Thermoplas cs are
becomes rigid when heated. Such a
organic materials that melt when heated.
material is also known as a thermoset or
They should be differen ated from
thermose ng polymer. Ini ally, the poly-
thermoset materials which cure or become
mer is a liquid or so solid. Heat provides
set, when they are heated. Thermoplas c
energy for chemical reac ons that increase
materials are melt processable, that is they
the cross-linking between polymer chains,
are formed when they are in a melted or
curing the plas c. The rate of curing may
viscous phase. This generally means they
be increasing in many cases by increasing
are heated, formed, then cooled in their
pressure or by adding a catalyst.
final shape.
Science-8 33