Page 118 - Science Class 07
P. 118
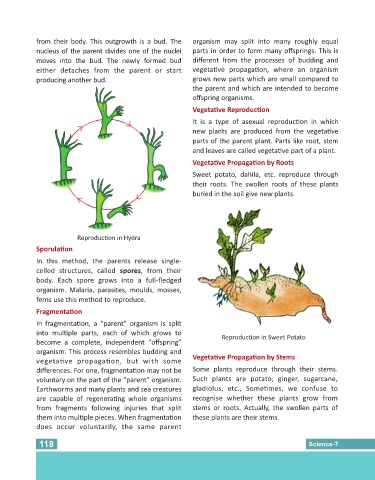
from their body. This outgrowth is a bud. The organism may split into many roughly equal
nucleus of the parent divides one of the nuclei parts in order to form many offsprings. This is
moves into the bud. The newly formed bud different from the processes of budding and
either detaches from the parent or start vegeta ve propaga on, where an organism
producing another bud. grows new parts which are small compared to
the parent and which are intended to become
offspring organisms.
Vegeta ve Reproduc on
It is a type of asexual reproduc on in which
new plants are produced from the vegeta ve
parts of the parent plant. Parts like root, stem
and leaves are called vegeta ve part of a plant.
Vegeta ve Propaga on by Roots
Sweet potato, dahila, etc. reproduce through
their roots. The swollen roots of these plants
buried in the soil give new plants.
Reproduc on in Hydra
Sporula on
In this method, the parents release single-
celled structures, called spores, from their
body. Each spore grows into a full-fledged
organism. Malaria, parasites, moulds, mosses,
ferns use this method to reproduce.
Fragmenta on
In fragmenta on, a “parent” organism is split
into mul ple parts, each of which grows to
Reproduc on in Sweet Potato
become a complete, independent “offspring”
organism. This process resembles budding and
vegeta ve propaga on, but with some Vegeta ve Propaga on by Stems
differences. For one, fragmenta on may not be Some plants reproduce through their stems.
voluntary on the part of the “parent” organism. Such plants are potato, ginger, sugarcane,
Earthworms and many plants and sea creatures gladiolus, etc., Some mes, we confuse to
are capable of regenera ng whole organisms recognise whether these plants grow from
from fragments following injuries that split stems or roots. Actually, the swollen parts of
them into mul ple pieces. When fragmenta on these plants are their stems.
does occur voluntarily, the same parent
118 Science-7