Page 185 - SST Class 06
P. 185
other hand, the untouchables were OUR FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS
denied social rights. The Right to
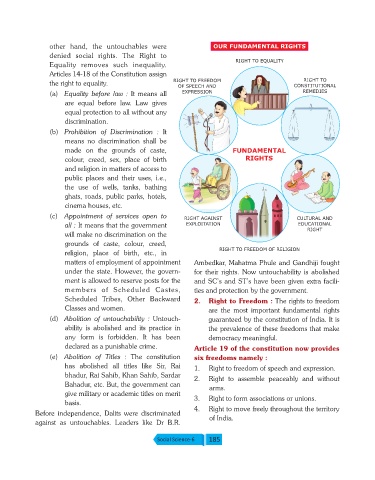
RIGHT TO EQUALITY
Equality removes such inequality.
Articles 14-18 of the Constitution assign
RIGHT TO
the right to equality. RIGHT TO FREEDOM CONSTITUTIONAL
OF SPEECH AND
(a) Equality before law : It means all EXPRESSION REMEDIES
are equal before law. Law gives
equal protection to all without any
discrimination.
(b) Prohibition of Discrimination : It
means no discrimination shall be
made on the grounds of caste, FUNDAMENTAL
colour, creed, sex, place of birth RIGHTS
and religion in matters of access to
public places and their uses, i.e.,
the use of wells, tanks, bathing
ghats, roads, public parks, hotels,
cinema houses, etc.
(c) Appointment of services open to RIGHT AGAINST CULTURAL AND
all : It means that the government EXPLOITATION EDUCATIONAL
RIGHT
will make no discrimination on the
grounds of caste, colour, creed,
RIGHT TO FREEDOM OF RELIGION
religion, place of birth, etc., in
matters of employment of appointment Ambedkar, Mahatma Phule and Gandhiji fought
under the state. However, the govern- for their rights. Now untouchability is abolished
ment is allowed to reserve posts for the and SC’s and ST’s have been given extra facili-
members of Scheduled Castes, ties and protection by the government.
Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward 2. Right to Freedom : The rights to freedom
Classes and women. are the most important fundamental rights
(d) Abolition of untouchability : Untouch- guaranteed by the constitution of India. It is
ability is abolished and its practice in the prevalence of these freedoms that make
any form is forbidden. It has been democracy meaningful.
declared as a punishable crime. Article 19 of the constitution now provides
(e) Abolition of Titles : The constitution six freedoms namely :
has abolished all titles like Sir, Rai 1. Right to freedom of speech and expression.
bhadur, Rai Sahib, Khan Sahib, Sardar
2. Right to assemble peaceably and without
Bahadur, etc. But, the government can
arms.
give military or academic titles on merit
3. Right to form associations or unions.
basis.
4. Right to move freely throughout the territory
Before independence, Dalits were discriminated
of India.
against as untouchables. Leaders like Dr B.R.
Social Science-6 185